Boolean operators
Boolean search examples
|
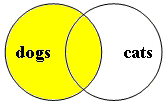
boolean search: dogs |
|
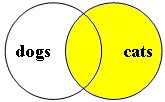
boolean search: cats |
|
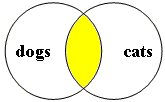
boolean search: cats AND dogs Searching on the Search Screen remember the default is AND, so do not type in the operator AND |
|
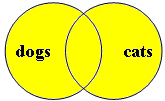
boolean search: cats OR dogs Searching from the Search Screen remember to type in OR in uppercase |
|
boolean search: cats NOT dogs Searching on the Search Screen page remember to type in the minus symbol (-) to represent the operator NOT |
REMEMBER: All searching in Libraries Australia is keyword based, unless quotation marks are used, eg. "wild dogs" which indicates a phrase search.
Boolean searches on the simple search screen
Boolean searches, AND, OR and NOT(-), are applied to all fields searched (eg. Title, subject, notes) from the simple search screen.
Order of precedence
Where a search query uses more than one operator, the Libraries Australia system, by default, processes them in the order: AND, OR, NOT
However you can make the system apply a different processing order by using parentheses. The terms in parentheses are then processed first of all, giving you a different search result.
Example 1
a search query: London or Paris vacation
- will by default search as: London OR (Paris AND vacation) - so Paris and vacation will be combined first and then records with the term London added into the result.
- but the same search query using parentheses around London or Paris: ie (London OR Paris) vacation - will search first for records with the term "London" and also for records with the term "Paris", then the system will select from the combined records all those which also contain the term " vacation".